Precision Matters: A Complete Guide to Measuring for SEPCO SAS Air Seals
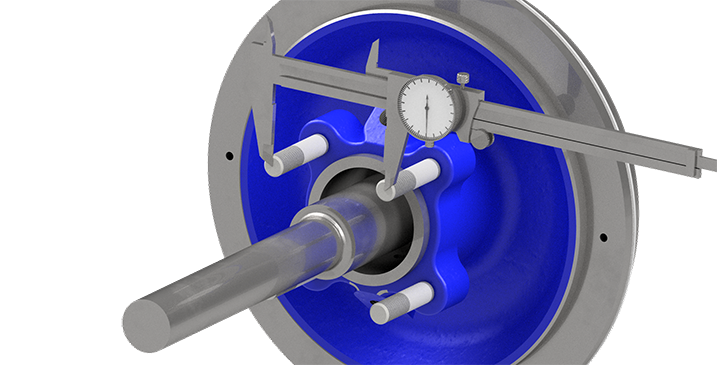 In the world of industrial equipment, where reliability and efficiency are paramount, the SEPCO SAS (Air Seal) stands out as a game-changer for applications involving powders, slurries, and other challenging materials. This non-contact pneumatic seal relies on precise airflow to create a barrier that prevents leaks, contamination, and equipment wear. But here’s the catch: even the smallest measurement error can lead to big problems like fitting/installing, premature failure, downtime, or safety hazards. Proper measurement isn’t just a best practice—it’s essential for maintaining pressure containment, handling shaft dynamics, and ensuring a clean, safe operation.
In the world of industrial equipment, where reliability and efficiency are paramount, the SEPCO SAS (Air Seal) stands out as a game-changer for applications involving powders, slurries, and other challenging materials. This non-contact pneumatic seal relies on precise airflow to create a barrier that prevents leaks, contamination, and equipment wear. But here’s the catch: even the smallest measurement error can lead to big problems like fitting/installing, premature failure, downtime, or safety hazards. Proper measurement isn’t just a best practice—it’s essential for maintaining pressure containment, handling shaft dynamics, and ensuring a clean, safe operation.
Whether you’re a maintenance engineer, plant operator, or someone diving into seal installations for the first time, this guide will walk you through why accuracy is critical and provide a step-by-step process to measure correctly. By the end, you’ll be equipped to avoid common pitfalls and achieve that perfect fit.
The Critical Role of Accurate Measurements
Imagine installing a seal that’s off by just a fraction of a millimeter. In a high-stakes environment like powder processing, this could mean uneven airflow, leading to leaks of hazardous particles or contamination of your product. The SAS’s design as a non-contact system makes it incredibly efficient and low-maintenance, but it demands tight tolerances for uniform performance. Inaccurate sizing not only shortens the seal’s lifespan but can also cause equipment damage, increased energy use, or even regulatory issues in sensitive industries.
From our experience (and backed by industry insights), skipping precise measurements is one of the top reasons seals underperform. Always prioritize tools like dial calipers or micrometers, and remember: clean your measurement areas first to eliminate debris that could skew readings. If in doubt, consult SEPCO’s documentation or reach out for custom engineering support—they’re experts in tailoring solutions.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure for an SAS Air Seal
Follow this consolidated process to ensure your measurements are spot-on. It’s designed for both replacements and new installations, and it emphasizes precision at every turn. Pro tip: Document everything as you go—it’ll save time if you need to verify with the manufacturer.
- Review Manufacturer’s Documentation
Start with the basics. Grab your pump or equipment manuals, note the model and serial numbers, and check spec sheets for recommended seal sizes and types (like solid or split SAS). This ensures compatibility and highlights any unique requirements. Skipping this step is like building a house without blueprints—risky! - Measure Shaft Diameter (or Sleeve OD)
Using a calibrated caliper or micrometer, gauge the shaft’s outer diameter at the seal location. Take multiple readings around the circumference and along the length to spot wear, taper, or irregularities. Precision here is key, as the SAS needs to hug the shaft just right without contact. - Measure Seal Chamber Bore Diameter
Shift to the stuffing box or seal chamber. Measure its inner diameter where the seal’s outer diameter (OD) will sit. Again, multiple points ensure uniformity—any ovality could compromise the seal’s fit.
- Measure Seal Chamber Depth (Gland Depth)
Employ a depth gauge or caliper extension to find the depth from the chamber’s outer face to the gland position. This dimension affects how the seal seats and compresses. - Measure Axial Length (Seal Face Width)
Determine the length along the shaft that the seal will occupy. This helps confirm the SAS can handle the available space without interference. - Check Shaft Runout and End Play
Bring out the dial indicator. Assess radial deflection (runout) and axial movement (end play). For a non-contact seal like the SAS, excessive values can disrupt airflow, so note these for potential adjustments.
- Document Operating Conditions
Don’t stop at physical measurements—record fluid type, temperature, pressure, RPM, and any abrasives or corrosives. These factors influence material choices and SAS design, ensuring longevity in real-world use. - Cross-Reference and Verify
Compare your data against the original seal (if available) or SEPCO’s PSS data sheet. If anything seems off, submit your details to SEPCO for expert confirmation. Better safe than sorry!
- Inspect and Calibrate Tools
Finally, double-check your tools. Zero calipers and micrometers, and use the ratchet on micrometers for consistent pressure. Regular calibration keeps your measurements reliable.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Once measured, the SAS installs straightforwardly with spacers for positioning and requires a stable air supply—check the pressure and flow regularly to ensure maintenance-free operation. If misalignment is a concern, opt for the SAS variant, which handles it gracefully.
In conclusion, investing time in accurate measurements pays off in spades with reduced downtime and enhanced safety. If you’re dealing with SAS seals, treat precision as your ally. Have questions or experiences to share? Drop a comment below—I’d love to hear how this guide works for you!
Note: Always refer to official SEPCO guidelines for the latest specs, as equipment standards can evolve.
 SEAL CONNECT
SEAL CONNECT Find Your Sealing Solution
Find Your Sealing Solution