Human Factors in Seal Failure: Operations and Maintenance
 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
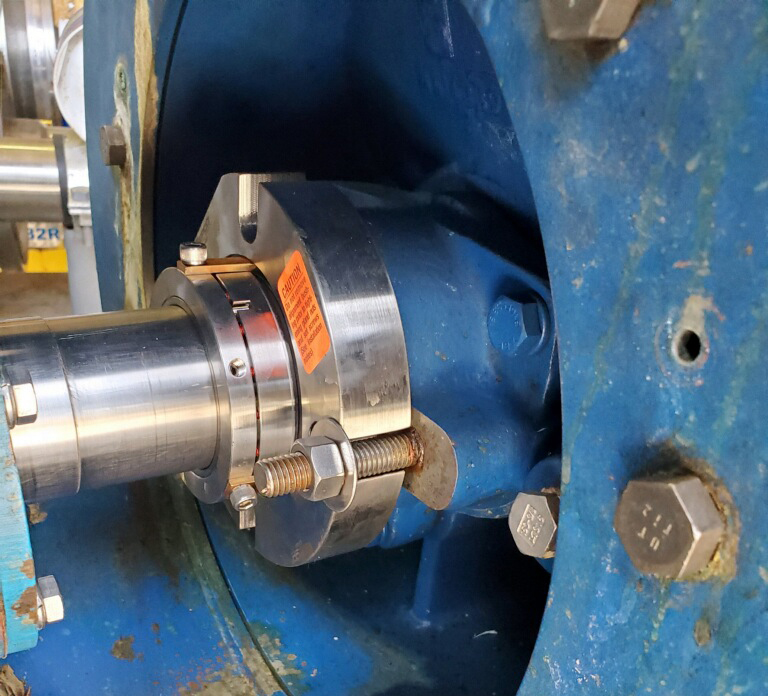
Mechanical seals are critical components in industrial equipment, such as pumps handling slurries, refiners, and grinders under pressure. They prevent leaks, contain pressures, and withstand abrasive materials. Failures result in downtime, spills, and safety risks. While material selection and design are important, human errors during installation and maintenance—such as misalignment, contamination, or excessive vibration—often contribute to catastrophic failure.
This article examines how enhanced maintenance training and ergonomic tools minimizes these errors. Building on standard checklists, it emphasizes human factors, incorporating real-world examples and metrics like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) to improve reliability in harsh conditions.
PROPER OPERATION PROCEDURES FOR INDUSTRIAL PUMPS
Industrial pumps, especially centrifugal models common in many applications, demand precise procedures for safe and efficient operation. Prioritize manufacturer manuals and site-specific protocols, adapting for pump type, fluid, and system. Operations teams require training, PPE (gloves, eye protection, hearing protection), and LOTO compliance. Obtain authorization and perform risk assessments for hazardous fluids.
PRE-START CHECKS
Conduct inspections to prevent damage, leaks, or dry running, which can ruin seals rapidly.
- Review documentation, obtain permissions, and confirm LOTO.
- Inspect system: piping, supports, instrumentation, pump-driver
alignment; ensure no strain and secure foundation. For new installs, verify hydro testing and submergence. - Check lubrication and seals: oil levels (1/2–2/3 sight glass), grease
fittings; adjust per specs and ensure seal lubrication. - Prime and vent: Fill pump and suction line, remove air. Use flooded or lift methods; vent seal chamber. Never start unprimed.
- Set valves: Open suction fully, close/partially close discharge; open cooling/sealing lines and confirm flow/pressure.
- Verify rotation: Manual turn for free movement; jog motor (coupled disconnected) for direction, then reconnect.
- Check electrical: voltage, amps, frequency; ensure driver readiness.
- Ensure cleanliness and gather tools.
STARTUP PROCEDURE
Minimize component stress during initiation.
- Start driver/motor.
- Slowly open discharge valve while monitoring pressure.
- Monitor for noises, vibrations, leaks, or spikes; confirm flow/head. Shut down if abnormal.
MONITORING DURING OPERATION
- Operate near best efficiency point (BEP) for longevity.
- Track parameters: pressure, flow, current (≤ motor rating), bearing temperatures (rise ≤35°C, max ≤75°C), vibrations, noise, seal leaks, oil levels.
- Avoid <30% design flow; use bypass if needed.
- Maintain cooling/sealing flow.
- Log data (temperatures, pressures, amps, conditions); keep area clean.
- For standbys: Prepare similarly; start new pump before stopping old for stable flow.
BEST PRACTICES AND SAFETY
- Avoid venting while running, frequent starts/stops.
- Integrate maintenance: Replace parts during shutdowns; change oil ~1500 hours or if contaminated.
- For solids/crystals: Rinse post-operation; drain in freezing conditions.
- Troubleshoot faults (e.g., blockages, air) promptly.
- Involve experts for initial starts; add safeguards for hazards.
Human Factors in Seal Failure
In industrial pumping systems, seal failures frequently stem from installation errors, such as contamination, face distortion, or improper torquing. Examples include dry starts warping components or impacts damaging couplings, leading to premature leaks. Vibration in refiners amplifies issues, allowing fibers to infiltrate and cause abrasion.
These problems intensify with fatigue, inadequate tools, or production pressures. Ergonomic deficiencies in repetitive tasks like seal insertion increase variability and failure rates. While checklists address basics (e.g., dimensions, cleaning, alignment), they overlook human strain. Focusing on ergonomics through training and tools mitigates these risks.
Maintenance Training Programs
Effective training equips teams to identify and prevent issues, embedding checklists into practice. Programs should cover seal fundamentals, failure analysis, and hands-on installation, tailored to slurries and contamination risks.
Key elements include:
- Basics: Seal types (cartridge vs. component), mechanics, and common failures (e.g., cracking, blistering).
- Hands-on: Disassembly, reassembly, and troubleshooting with mill-simulating mock-ups.
- Root cause analysis: Techniques like five whys, linked to metrics (MTTR, MTBF) for continuous improvement.
- Ongoing: Certifications and refreshers, especially in high-turnover environments.
In supported projects, trained teams reduced installation errors by ~30%, improving seal performance in fibrous applications and enhancing overall reliability.
ERGONOMIC INSTALLATION TOOLS
Ergonomic tools complement training by reducing physical demands and improving precision. In confined, vibrating environments, tools like non-slip hydraulic pushers and multi-jaw grippers prevent damage to O-rings and faces.
Recommended tools:
- Twisters and pushers: Ergonomic handles for seal insertion without strain, ideal for U-cups in pumps.
- Disassembly kits: Sized for various rings (O, X, U) to enable clean extraction and minimize contamination.
- Aids: Inflatable or mechanical devices for consistent, rapid installation under pressure.
These ensure proper lubrication and alignment, reducing fatigue and errors in debris-prone settings.
METRICS ON MTBF IMPROVEMENTS
MTBF quantifies reliability gains from addressing human factors. Field data indicates significant extensions by minimizing errors.
| Intervention | Typical MTBF Boost | Generic Industrial Example |
| Maintenance Training | 20–50% | Reduced failures in high-pressure hot water pumps, extending MTBF from 6 months to >18 months. |
| Ergonomic Tools | 15–40% | Minimized errors in refiners, adding 25% via precise alignment. |
| Combined Approach | 50–100%+ | Integrated programs doubled MTBF in challenging environments, with rapid ROI. |
These improvements stem from fewer premature failures, confirmed by root cause analyses showing reduced human error in high-vibration mills.
CONCLUSION
Integrating robust training and ergonomic tools with checklists directly addresses human errors in pump and seal maintenance, yielding substantial MTBF gains and operational efficiency. SEPCO supports implementation for long-term reliability. Contact www.sepco.com for tailored guidance.
 SEAL CONNECT
SEAL CONNECT Find Your Sealing Solution
Find Your Sealing Solution